

Customer relationship management (CRM), calendaring, e-mail and human resources management are among some of the more common applications delivered as services from the cloud infrastructure.įor IT departments, IT service management, spam filtering, intrusion prevention and other traditional security software are among the application types increasingly available via the SaaS model. A business can find just about any general office application available via the SaaS model. Often geared toward the end user who needs access through a web browser or other thin clients, SaaS provides access to applications hosted on a service provider’s cloud infrastructure. The richest PaaS offerings enable an organization to support the entire application development lifecycle.
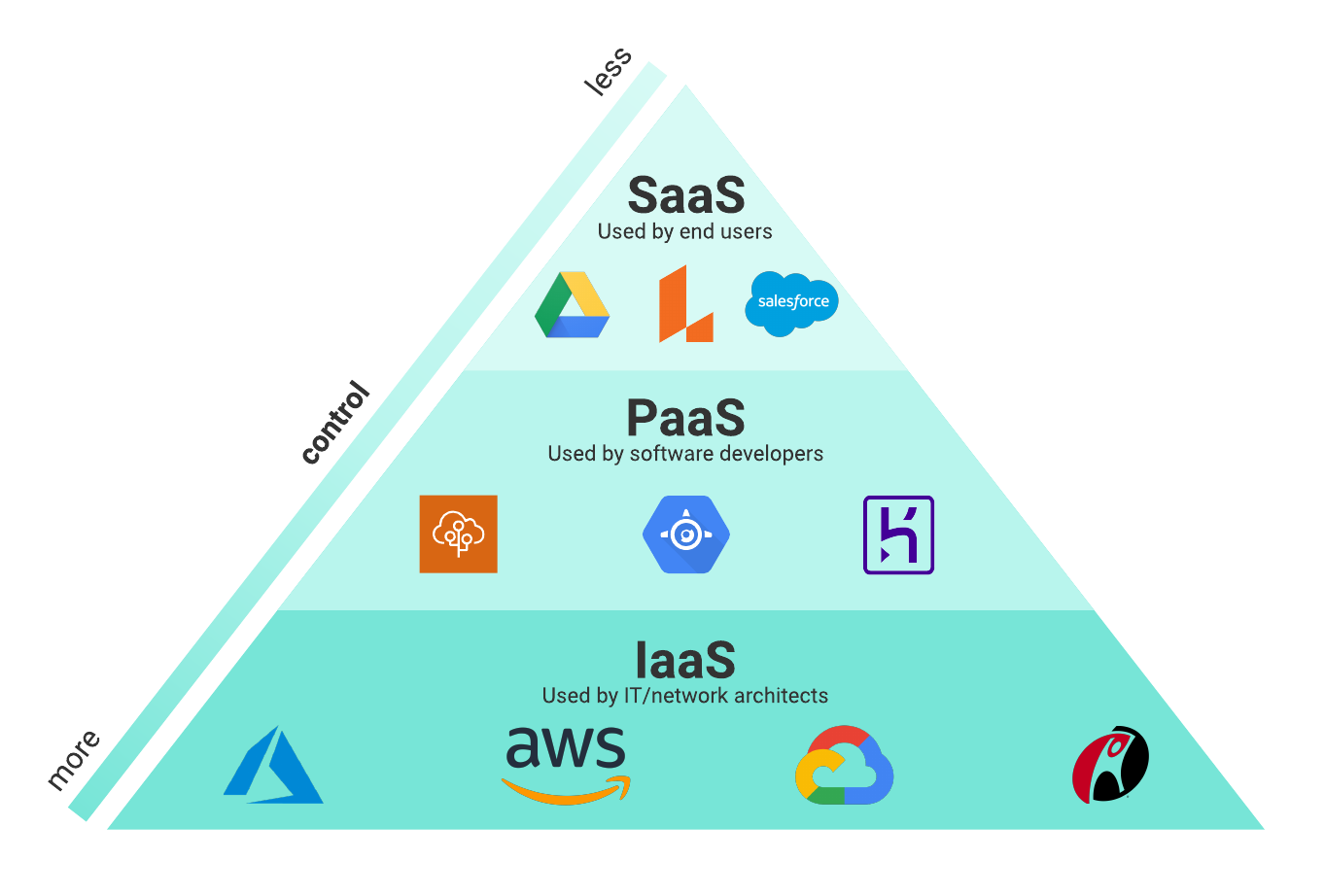
Although being able to tweak the application may make the SaaS model more attractive, the catch is that when combined with a PaaS offering, SaaS becomes less portable. For example, some cloud companies offer a PaaS and SaaS combo, providing organizations with the ability to customize the packaged application. The types of PaaS offerings vary which option works best for a business depends on its goals. The user organization has application control, the caveat in many cases being that the developers must be comfortable with the PaaS provider’s choices for programming languages, interfaces, development tools, database support and the like. With PaaS, a company can deploy applications without incurring the associated upfront provisioning and ongoing maintenance and management costs of the underlying infrastructure. Rather than simply delivering prepackaged applications via the on a service model, a PaaS provider offers up the entire computing platform and solutions stack needed for an application runtime environment. They have no way of controlling the types of virtual resources running atop the infrastructure they’ve provisioned from the cloud.ĭerived from the SaaS model, PaaS caters to developers’ needs. IT shops must keep in mind, however, that multi-tenancy applies across the public cloud infrastructure. In other words, organizations can increase productivity while eliminating under utilization costs. Infrastructure as a Service is similar in concept to a traditional dedicated hosting service, with two major differences: Organizations tap into a shared, highly scalable pool of resources, and they pay for only what’s used on a utility basis. The cloud service provider manages the infrastructure, including any Scaling up or down as needed. While a user company can run applications, databases, operating systems and other software on top of its selected infrastructure, it has no direct control over or access to those machines. – from a cloud services provider, often via a self-service catalog. Rather, the business obtains needed IT infrastructure – servers, security, storage, networks, etc. This service model enables user organizations to forgo deployment of new datacenter equipment to handle growing operational needs. Determining The Cost Of The Cloud Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
